Setting up Slash commands for Slack workspace
Slack has become one of the most popular chat and collaboration tool in software industry. Slack offers all kinds of custom integration, third party apps and a huge scope for automation of trivial every tasks.
In this post, we will try to set up a slash command /hello for our slack workspace that makes a request to a REST API and displays response back on the slack channel.
The REST API can then trigger other APIs, automate something trivial like initiating a project build or even book an uber.
Here’s how the slash command is supposed to works once we’re done with setup:
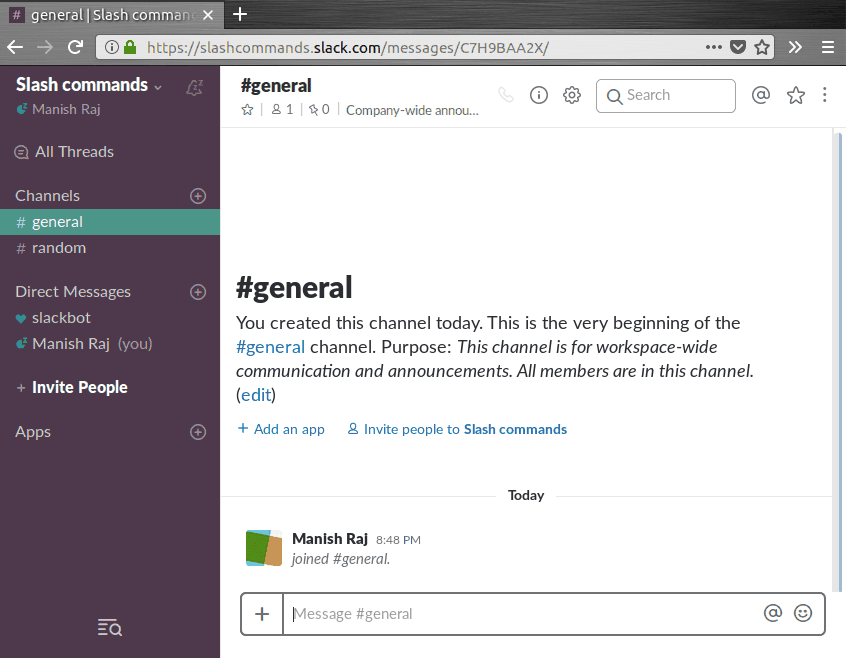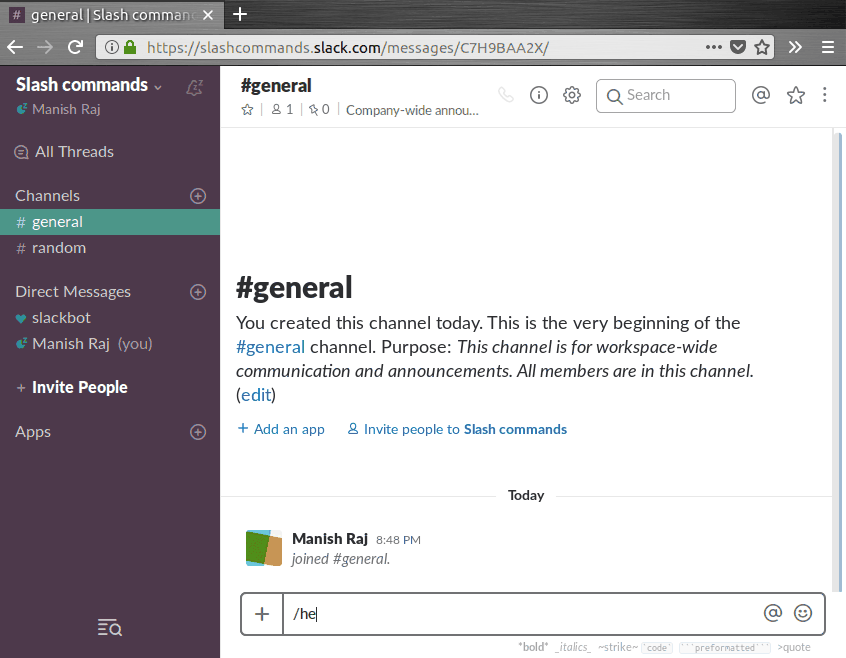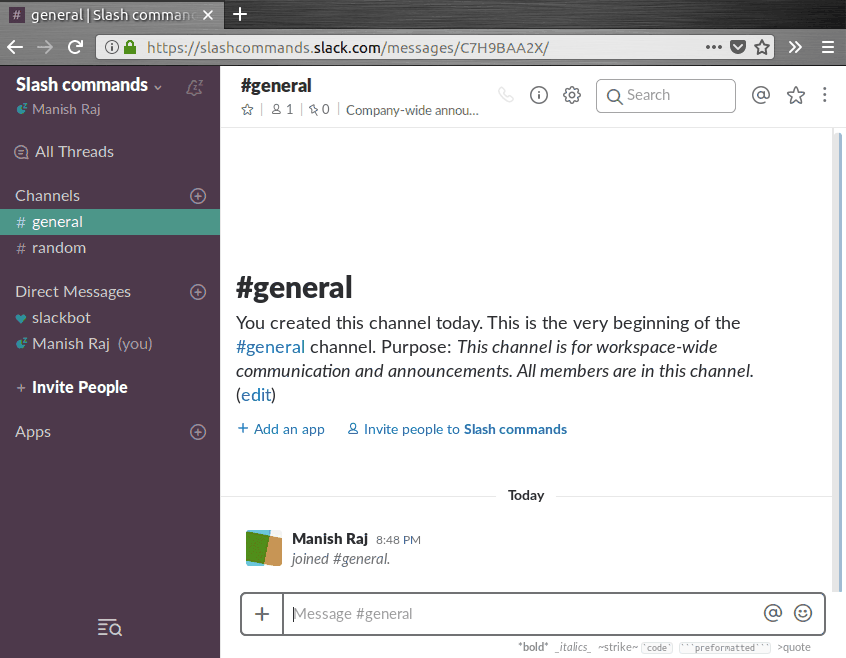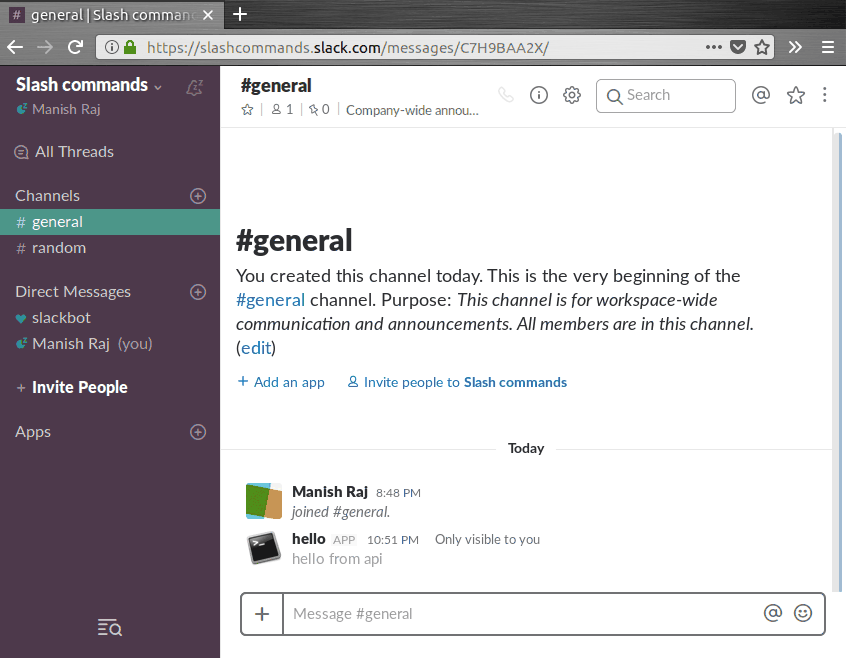
Alright, let’s get started.
Deploy API service
Begin by deploying your API service on the Internet. I used heroku since it offers five free dynos (application containers).
I forked the sample nodejs app and built a dummy API service that leverages heroku’s one-click deploy.
The project is available at: https://github.com/androidfanatic/slash-cmd-api
It is a simple API service that returns hello from api when one makes a GET request to /hello endpoint.
The deployed service is available at: http://slash-cmd-api.herokuapp.com/hello
Add a slash command to slack workspace
Now that you have your API service deployed on cloud, let’s begin configuring slack workspace and add a slash command that calls the API.
If you don’t already have a workspace on slack, signing up for one is very easy and quick.
Once you’re inside the workspace, click on workspace name on top left and go to: Workspace Settings > Configure App > Browse the App Directory.
Search for “Slash Commands” and click on it.
Add a new config for “slash commands” app based on your API specs such as url endpoint, request method, slash command name etc.
For me, config looks something like this:
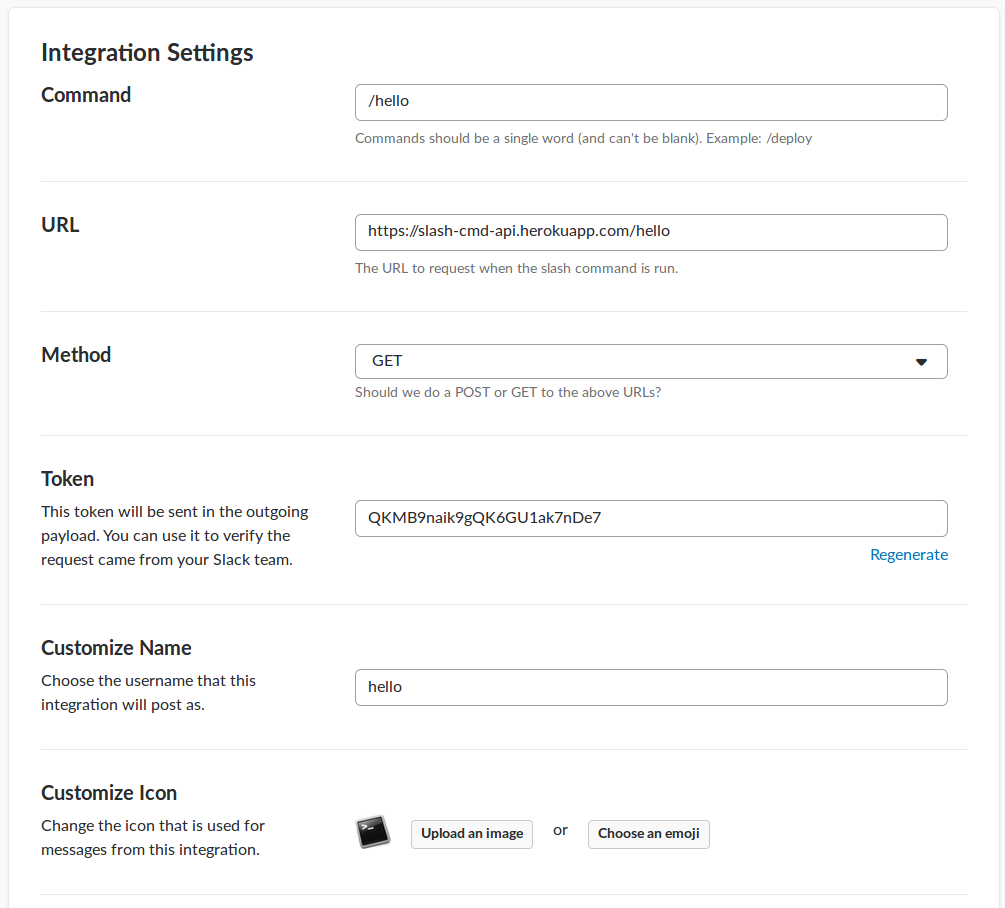
Make sure to get the HTTP URL and request method right. Slack also displays a randomly generated token which can be used to verify and accept requests to your API originating only from slack.
Click on save integration and go back to any channel to test if the slash command works.
Congrats, you just set up a very basic slash command.